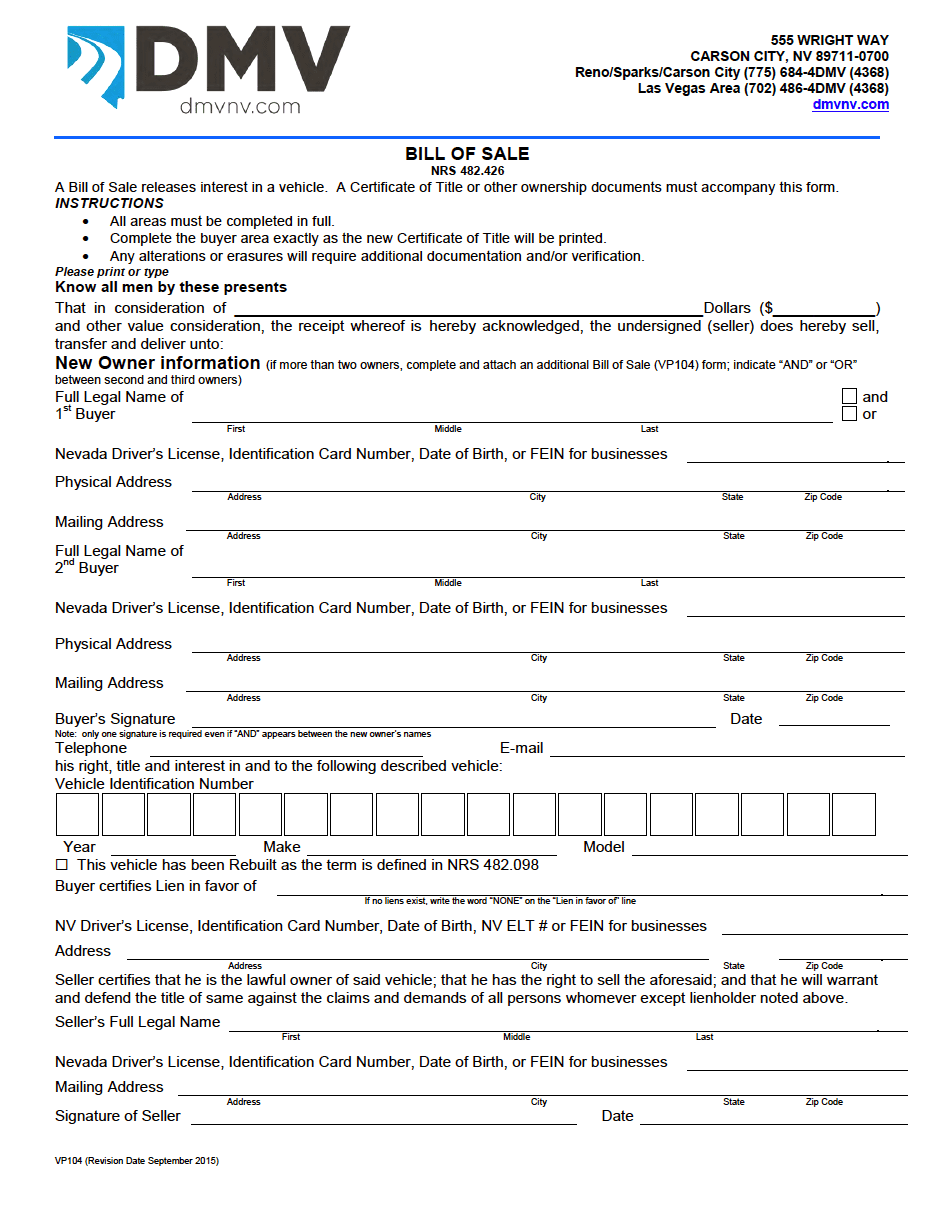
Nevada Motor Vehicle Bill of Sale Form
A Nevada motor vehicle bill of sale form relieves the seller from ownership and transfers possession to the buyer. The Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) requires both parties to fill out each section with the most up-to-date information possible. This requirement includes the car’s value, vehicle identification number (VIN), year, make, and model. Buyers and sellers must also disclose rebuilt vehicles and if a lien existed. In this case, the individuals may need to take additional steps before the transaction can occur.
|
What is a Nevada Car Bill of Sale?
A Nevada car bill of sale supports the title to prove a change in vehicle liability. The title and bill of sale cannot stand alone, meaning that the buyer and seller must finalize and safely store both documents. Each owner (or co-owner) must enter identifying information, such as their driver’s license number, identification card number, date of birth, or FEIN (businesses only). In addition, they must provide their physical and mailing addresses, telephone number, email, signature, and dates. The DMV does not accept an unfinished or altered bill of sale form; therefore, both parties must ensure they have completed it before submission.
What are the Buyer’s Tasks?
A potential buyer must research the vehicle’s history before purchasing. This process ensures they buy a car without mechanical issues, preventing additional expenses. Individuals can obtain this information using the following websites: NMVTIS title information, NICB VIN check, NHTSA VIN decoder, and Safety Recall Lookup.
Per state law, the purchaser cannot take the seller’s plates. Instead, the merchant needs to remove them before officially transferring ownership. The new owner can drive the newly purchased car without a movement permit for three (3) days if they have proof of possession and insurance. Then, they must obtain a movement permit from their nearest DMV office.
Buyers must register their vehicle with their local DMV office within thirty (30) days of purchasing. A third party can register the car if they have an application signed by the owner or an original, notarized power of attorney (motor vehicle or general only).
Dealer Sales
Nevada does not have a “cooling off” period, which means dealers sell used vehicles “as is,” and all contracts are final. Therefore, buyers must understand all information in the agreement(s) and ensure its completion before signing.
Purchasers should not purchase the vehicle unless the dealer provides 1) copies of the contract(s), 2) a temporary thirty (30) day registration permit, 3) proof of passed emissions inspection and 4) an electronic dealer report of sale (EDRS). If the vehicle has 75,000 or more miles, they must also give the buyer a drive train inspection report.
What are the Seller’s Tasks?
Sellers must conduct the sale on residential property in Nevada. The state does not allow them to park or offer it in empty lots or public property, except with special permission. Furthermore, they cannot sell more than three (3) cars in their name within a year without a dealer’s license. Salvage vehicles must have a proper title after being built and inspected, and the seller must notify the buyer of the car’s history.
Local law prohibits individuals from subleasing their vehicle payments or having someone take over the loan without approval. Sellers must pay off the lien or loan on their vehicle before transferring it.
Car owners must have the title during the transaction. If they do not have the title, they must apply for a duplicate by completing an application (VP 012). Then, both parties must complete the appropriate parts of the form and sign their names. Per state law, the merchant must disclose the odometer reading on the title if the car has the model year 2011 or newer.
Transferors must collect their license plates from the vehicle, as the buyer cannot take or use the seller’s plates. Instead, they must obtain new ones from the state during registration. They should complete and retain the bill of sale as a transfer record. In addition, the individual must notify the DMV of the transaction to remove their liability. To carry out this task, they complete the Registration Cancellation & Vehicle Resale Notification.
How to Register a Car in Nevada (6 Steps)
Residents have thirty (30) days to bring their newly purchased vehicle to the DMV. During the appointment, they obtain a title, registration, and license plates for the car. The office also permanently records the transfer of ownership in its database.
Step 1 – Insurance
Nevada drivers must have car insurance and safely store the card (or other proof of the plan) in the vehicle. They must show law enforcement, or other officials, the information upon request.
For approval, the insurance coverage must be from a Nevada-licensed carrier in a name that matches the registration and title. The effective date must be on or before the registration date.
Per state law, Nevada residents must have $25,000 of coverage for the bodily injury or death of one (1) person and $50,000 for two (2) or more. The plan must also include $20,000 for each incident of property destruction.
Step 2 – VIN Inspection
The owner must have their VIN inspected if the vehicle has never had a title or registration in Nevada. Depending on the facility, DMV offices carry out the inspections, which may or may not require an appointment.
Inspections must happen before registration so the owner can bring the information to their title and tag appointment. More specifically, they must provide the form (VP 015) completed and signed by the law enforcement officer.
Step 3 – Title
Sellers must record the vehicle’s mileage during the sale if it has the model year 2011 or newer. The requirement still applies, even if the title exempts the car after nine (9) years. If the owner does not need to disclose the odometer reading, they must check the “exempt” box.
New vehicles from the dealer do not necessitate the buyer to take action. Instead, the dealership must apply for the title, which arrives by mail to the customer within six (6) weeks. In the meantime, the new car owner must have the manufacturer’s certificate of origin (MCO) or bill of sale to verify their purchase.
Used vehicle sales require the buyer to visit the DMV for titling purposes. They must bring the completed and signed title from the seller to confirm the ownership transfer and pay the fees.
If applicable, the registrar must provide a Payment Authorization Form (ADM 205) and Lien Release (VP 186). Standard shipping takes six (6) weeks; however, the applicant can complete an Application for Expedited Processing/Shipping (VP 265) to speed up the process.
Step 4 – Emissions Inspection
Nevada law requires vehicles to undergo an annual emissions inspection. Residents can use the Station Search tool to discover emissions locations, repair businesses, and renew their registration. Dealerships must handle emissions testing, whereas private sales require the buyer to have the car inspected.
The vehicle needs an emissions inspection if it is:
- Registered in Clark or Washoe county (urban areas only);
- Powered by gas;
- Powered by diesel and weighs 14,000 pounds or less;
- The model year of 1968 or newer;
- A gas-powered vehicle (purchased new) at its fourth registration; and/or
- A hybrid vehicle (bought new) at its fifth registration.
The test form lasts ninety (90) days if the vehicle passes inspection. The owner must bring the document to their DMV registration appointment within that time frame. Note that passed emissions inspections from dealers expire after one hundred and eighty (180) days.
Step 5 – Registration
The Nevada DMV allows established residents to register their recently purchased vehicle online or at an office. New residents must transfer their registration in person.
Registrars using the Carson City, Henderson, Las Vegas, or Reno offices must make an appointment. Third parties can register the vehicle for the owner with a signed application (VP 222) or power of attorney (VP 136).
When registering online (via the DMV app or myDMV), individuals must provide the report of sale or lease, current mileage, current registration, and tax exemption number (if applicable). The registrar must also print the permit and receipt at home, as the DMV does not mail the information.
In-person registrations require a report of sale or lease, a current Nevada insurance card, current odometer reading, a Nevada emission vehicle inspection report (if applicable, issued by the dealer), and the current registration. The individual must bring their license plates (if they wish to surrender them) and the appropriate forms for obtaining personalized or specialized plates (if desired).
Step 6 – Renew
Nevada requires annual registration renewals, meaning owners must reapply by the date listed on the active registration. The state sends a postcard with the necessary information thirty (30) days before expiration. Individuals who opted for email notices will not receive a physical mailing. Nonetheless, residents must renew on time, even if they did not receive a postcard or email.
The DMV assesses late fees for renewals that occur after the deadline. Owners who fail to renew on time, but need to operate their vehicle, can apply for a temporary movement permit online or in person.
State law mandates yearly smog checks (i.e., emissions inspections). When renewing in person or online, the resident must provide proof of the emissions test, an unexpired insurance card, and payment.