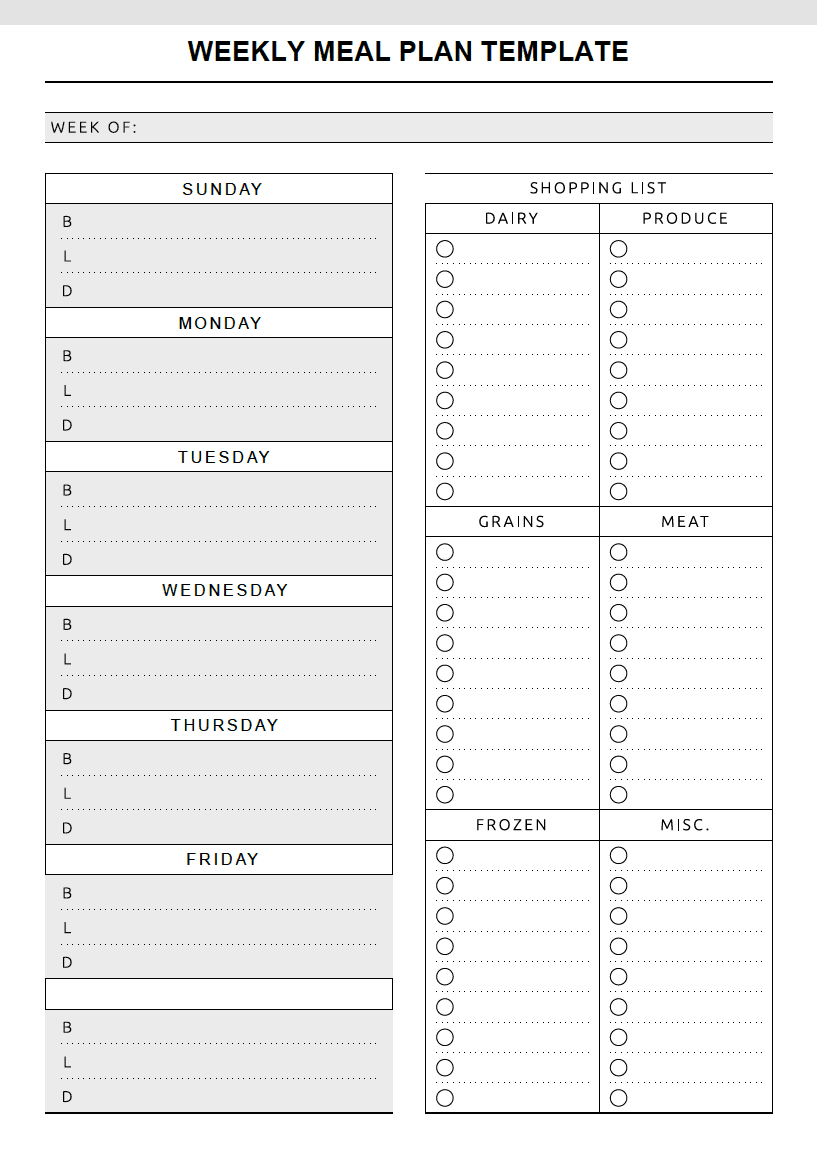
Meal Planning Templates
A meal planning template is a form used for tracking and monitoring one’s meals on a daily, weekly, and/or monthly basis. The act of planning meals allows for organization and structure as it removes the guesswork for the required ingredients and supplies. It also provides a base to create a grocery list and can be helpful to monitor calories. When completing the template, enter a meal for each day and fill in any additional fields pertaining to the plan.
Meal Plan Templates

1. PDF | Word (.docx)
2. PDF | Word (.docx)
3. PDF | Word (.docx), ODT
4. PDF
What is a Meal Plan?
A meal plan is a template to schedule meals during a set amount of time. One may use it to reference which foods will be eaten on a certain day. The plan can also be tailored to individual preferences and needs, such as allergies and specific diets, or accommodate different family sizes.
Meal plans are cost-effective and promote healthier eating. Having a concrete system in place means that there is no question of what to eat or when to eat it. This knowledge will help to save calories and money since they can be calculated beforehand.
Weekly Meal Plan Templates
5. PDF | Word (.docx)
6. PDF
7. PDF | Word (.docx)
8. PDF, Word (.docx), ODT
Guide to Meal Planning
Step 1 – Select a Plan
Meal plans vary based upon desires and needs. Each plan should accommodate personal preferences, as some may be more detailed or include unique categories.
Choose a daily, weekly, or monthly template, and download or print it to fill it in.
Step 2 – Fill in Meal Plan Sections
The primary use of a meal plan is to schedule foods in advance. For each meal, enter a recipe name, or designate the section for leftovers or takeout.
Step 3 – Choose Recipes and Write Down Ingredients
Compile a list of recipes, and enter them into each meal section. The meal planner should only choose recipes that will accommodate their needs. Consider these factors when planning:
- Household Size
- Food Preferences
- Finances and Budgeting
- Health Status
- Food Waste
- Preparation and Cooking Time
- Level of Recipe Difficulty (or Cooking Experience)
Step 4 – Create a List and Grocery Shop
Write down all ingredients needed to make the desired recipes. Transfer this information into a grocery list, and shop ahead of time to ensure that all foods are on hand before cooking.
Step 5 – Prepare Foods
Review all recipes and take note of anything that can be chopped, marinated, frozen, or thawed before making the meal. Be sure to refrigerate or freeze all foods according to USDA Food Safety Guidelines to prevent food poisoning.
Monthly Meal Plan Calendars
9. PDF | Word (.docx)
10. PDF | Word (.docx)
11. PDF
12. PDF
Losing Weight with Meal Plans
Meal plans provide a way to count calories, which promotes weight loss. Choose recipes or foods that have minimal calories or that fit into a daily budget. In addition to selecting the right recipes, it is important to monitor the calories for each portion of food. Use the meal plan to track the totals for each meal to monitor daily intake and lose weight.
Learn more about healthy eating by researching the ideal foods. Find websites that promote health and offer recipes that align with these values. Many authors include calories or nutrition information for each recipe, which can be transferred into the meal plan. However, recipes that are not healthy can also be used. In these cases, swap out unhealthy ingredients and choose ones that are lower-calorie.
This same concept applies to takeout meals. Select restaurants that have mindful options or that provide the calorie information. If this information is not available, use a calorie tracker to calculate an estimate.
Blank Meal Plan Templates
13. PDF | Word (.docx)
14. PDF | Word (.docx)
15. PDF | Word (.docx)
16. PDF, Word (.docx)
Tips for Meal Planning on a Budget
Planning meals saves money. Follow these tips when creating a meal plan:
- Opt for recipes with fewer ingredients. Simple meals use basic ingredients that are universal. Since they are generic products, they also cost less and decrease the amount spent on each recipe.
- Buy in bulk. Purchasing food in greater quantities lowers the cost because companies spend less to package and ship it. Stores are then able to sell the food at a cheaper rate. When rates are lower for stores, the products can be offered to consumers at discounted prices.
- Store and reheat leftovers. Leftovers can be stored for another meal. They can also be frozen and served months later. To batch prep, increase the ingredients of each recipe and store for upcoming meals. Limit ingredient variety to make it more cost-efficient, especially when cooking in bulk.
- Select cheaper versions. Use brand name versions of each food product, and choose frozen produce as it is cheaper than fresh and contains just as many nutrients. Other ways to save are using canned fish or chicken and choosing less expensive substitutes for costly ingredients. Shopping local also tends to be less pricey.
- Choose recipes with similar ingredients. Although variety can be important, it is more cost-effective to choose only one or two cuisines per week, as they have comparable ingredients. To save even further and minimize food waste, cook similar meals back-t0-back so the ingredients do not spoil.
- Plan for more homemade meals than takeout. Restaurants charge more than grocery stores because they have to pay employees and other fees. However, that does not mean that takeout is off-limits. Planning the restaurant (or even meal) ahead of time can provide a clearer view of how much it will cost.
Sample Meal Plan Templates
17. PDF | Word (.docx)
18. PDF | Word (.docx)
19. PDF | Word (.docx)
20. PDF, Word (.docx), Excel (.xlsx)